AT THE ORIGINS OF THE HUMAN KIND. PRESENTATION ON THE SUBJECT “WORLD HISTORY OF RUSSIA AND THE WORLD FROM ANCIENT TIMES TO THE END OF THE 19TH CENTURY. EVG 3097@MAIL. RU

 BASIC CONCEPTS AND TERMS. EVOLUTION, ABSTRACT THINKING, PRIMITIVE HERD, INTERSPECIES AND INTRASPECIES STRUGGLE. EARLY PALEOLITHIC, NEANDERTHAL, CRO-MANNON. RACES OF PEOPLE, MESOLITHIC, ROCK PAINTING, FETISHISM.
BASIC CONCEPTS AND TERMS. EVOLUTION, ABSTRACT THINKING, PRIMITIVE HERD, INTERSPECIES AND INTRASPECIES STRUGGLE. EARLY PALEOLITHIC, NEANDERTHAL, CRO-MANNON. RACES OF PEOPLE, MESOLITHIC, ROCK PAINTING, FETISHISM.
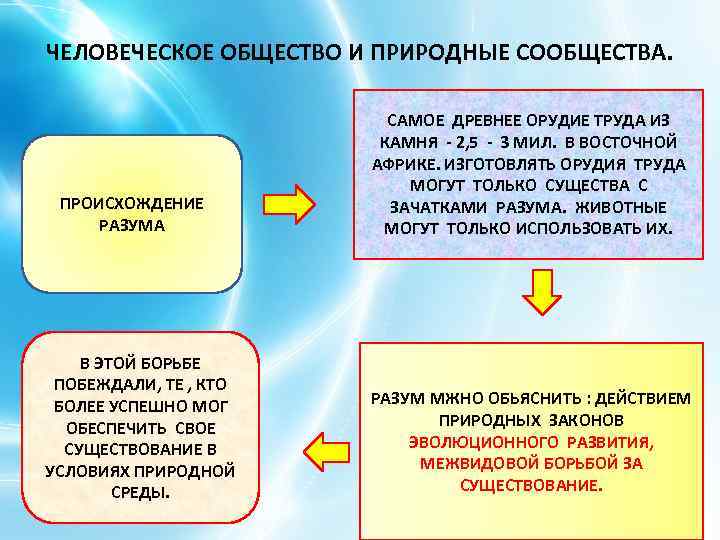 HUMAN SOCIETY AND NATURAL COMMUNITIES. ORIGIN OF MIND IN THIS STRUGGLE, THOSE WHO COULD ENSURE THEIR EXISTENCE IN THE CONDITIONS OF THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT WON MORE SUCCESSFULLY. THE MOST ANCIENT STONE TOOL - 2.5 - 3 MIL. IN EAST AFRICA. ONLY BEINGS WITH THE RUDGES OF MIND CAN MAKE TOOLS OF LABOR. ANIMALS CAN ONLY USE THEM. REASON CAN BE EXPLAINED: BY THE OPERATION OF NATURAL LAWS OF EVOLUTIONARY DEVELOPMENT, INTERSPECIES STRUGGLE FOR EXISTENCE.
HUMAN SOCIETY AND NATURAL COMMUNITIES. ORIGIN OF MIND IN THIS STRUGGLE, THOSE WHO COULD ENSURE THEIR EXISTENCE IN THE CONDITIONS OF THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT WON MORE SUCCESSFULLY. THE MOST ANCIENT STONE TOOL - 2.5 - 3 MIL. IN EAST AFRICA. ONLY BEINGS WITH THE RUDGES OF MIND CAN MAKE TOOLS OF LABOR. ANIMALS CAN ONLY USE THEM. REASON CAN BE EXPLAINED: BY THE OPERATION OF NATURAL LAWS OF EVOLUTIONARY DEVELOPMENT, INTERSPECIES STRUGGLE FOR EXISTENCE.
 HUMAN EVOLUTION. FORMATION OF THE RUDIGIES OF SOCIAL BEHAVIOR. THE ABILITY TO LEARN HAS MADE AWAY A PERSON WHO TRANSFERED EXPERIENCE FROM GENERATION TO GENERATION, UNLIKE ANIMALS WHO COULD NOT DO THIS. THE ACCUMULATION OF KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS, MASTERING FIRE ALLOWED HUMANS TO UNITED INTO HERDS IN PRIMITIVE COMMUNITIES TO EXIST SUCCESSFULLY AND PEOPLE COULD PROTECT THEMSELVES AND CHILDREN. IN NATURE. THE INTER-SPECIES STRUGGLE WON THOSE WHO HAD THE ABILITY TO COMMUNICATE AND COORDINARY ACTIONS. FORMATION OF SPEECH HAS COMPLICATED THE BRAIN STRUCTURE. THE ABILITY TO ABSTRACT THINKING HAS APPEARED. EACH STAGE OF HUMAN EVOLUTION IS CONNECTED FIRST WITH THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE BRAIN, AND SECONDLY WITH THE IMPROVEMENT OF WORK TOOLS.
HUMAN EVOLUTION. FORMATION OF THE RUDIGIES OF SOCIAL BEHAVIOR. THE ABILITY TO LEARN HAS MADE AWAY A PERSON WHO TRANSFERED EXPERIENCE FROM GENERATION TO GENERATION, UNLIKE ANIMALS WHO COULD NOT DO THIS. THE ACCUMULATION OF KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS, MASTERING FIRE ALLOWED HUMANS TO UNITED INTO HERDS IN PRIMITIVE COMMUNITIES TO EXIST SUCCESSFULLY AND PEOPLE COULD PROTECT THEMSELVES AND CHILDREN. IN NATURE. THE INTER-SPECIES STRUGGLE WON THOSE WHO HAD THE ABILITY TO COMMUNICATE AND COORDINARY ACTIONS. FORMATION OF SPEECH HAS COMPLICATED THE BRAIN STRUCTURE. THE ABILITY TO ABSTRACT THINKING HAS APPEARED. EACH STAGE OF HUMAN EVOLUTION IS CONNECTED FIRST WITH THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE BRAIN, AND SECONDLY WITH THE IMPROVEMENT OF WORK TOOLS.
 1. RELIGION APPROVES THE DIVINE ORIGIN OF MAN. STAGES OF HUMAN BEHAVIOR. 2. IN THE 20TH CENTURY THE VIEW THAT MAN IS A PRODUCT 2.5 – 3 mil. EAST AFRICA – AUSTRALOPITHECICA. USE OF TOOLS, WALKING UPREMODERN SCIENCE DOES NOT HAVE THE ANSWER WHY THIS HAPPENED. HENCE THE DIFFERENCE OF VIEWS ON THE ORIGIN OF THE ANCESTOR OF MODERN MAN. APPROXIMATELY 1.5 – 700 THOUSAND. YEARS AGO EVOLUTION. EARLY PALEOLITHIC. 3. IN THE 21st CENTURY THEORY ABOUT EXTRATERRESTRIAL TOOLS – SCRAPS, CUTS FROM THE ORIGIN OF BONE AND STONE. UPREAMING, INCREASING BRAIN VOLUME FROM 300 – 600 CU. CM UP TO 1300 – 1700 CU. SEE NEANDERTHALS. APPROXIMATELY 200 – 300 THOUSAND. YEARS AGO - MASTERING FIRE. THE EARLY PALEOLITHIC TIME ENDS WITH THE ADVANCE OF GLACIERS ABOUT 20 - 30 thousand years ago. YEARS AGO THE NEANDERTHALS COMPLETELY DISAPPEARED. CRO-MANNON CONFIRMED.
1. RELIGION APPROVES THE DIVINE ORIGIN OF MAN. STAGES OF HUMAN BEHAVIOR. 2. IN THE 20TH CENTURY THE VIEW THAT MAN IS A PRODUCT 2.5 – 3 mil. EAST AFRICA – AUSTRALOPITHECICA. USE OF TOOLS, WALKING UPREMODERN SCIENCE DOES NOT HAVE THE ANSWER WHY THIS HAPPENED. HENCE THE DIFFERENCE OF VIEWS ON THE ORIGIN OF THE ANCESTOR OF MODERN MAN. APPROXIMATELY 1.5 – 700 THOUSAND. YEARS AGO EVOLUTION. EARLY PALEOLITHIC. 3. IN THE 21st CENTURY THEORY ABOUT EXTRATERRESTRIAL TOOLS – SCRAPS, CUTS FROM THE ORIGIN OF BONE AND STONE. UPREAMING, INCREASING BRAIN VOLUME FROM 300 – 600 CU. CM UP TO 1300 – 1700 CU. SEE NEANDERTHALS. APPROXIMATELY 200 – 300 THOUSAND. YEARS AGO - MASTERING FIRE. THE EARLY PALEOLITHIC TIME ENDS WITH THE ADVANCE OF GLACIERS ABOUT 20 - 30 thousand years ago. YEARS AGO THE NEANDERTHALS COMPLETELY DISAPPEARED. CRO-MANNON CONFIRMED.
 BUT THEY ALL RELATE TO THE SAME TYPE OF HOMOS SAPIES. MAIN RACES OF PEOPLE. RACIAL CHARACTERISTICS ARE DIVERSE: SKIN PIGMENTATION, EYE SHAPE, HAIR COAT, HEIGHT, BLOOD TYPES, ETC. NEGROID RACE. (skin pigmentation, curly hair, weak beard and mustache growth) EUROPEAN RACE. (soft hair, protruding nose) MONGOLID RACE. (eye shape, cheekbones, straight hair) OCEANIC RACE. (a combination of Negroid and Caucasian features) LARGE RACES ARE HETEROGENEOUS. IN ADDITION TO THIS, TRANSITIONAL RACES HAVE BEEN DEVELOPED AT THE BORDERS OF RACES.
BUT THEY ALL RELATE TO THE SAME TYPE OF HOMOS SAPIES. MAIN RACES OF PEOPLE. RACIAL CHARACTERISTICS ARE DIVERSE: SKIN PIGMENTATION, EYE SHAPE, HAIR COAT, HEIGHT, BLOOD TYPES, ETC. NEGROID RACE. (skin pigmentation, curly hair, weak beard and mustache growth) EUROPEAN RACE. (soft hair, protruding nose) MONGOLID RACE. (eye shape, cheekbones, straight hair) OCEANIC RACE. (a combination of Negroid and Caucasian features) LARGE RACES ARE HETEROGENEOUS. IN ADDITION TO THIS, TRANSITIONAL RACES HAVE BEEN DEVELOPED AT THE BORDERS OF RACES.
 MAN IS DEVELOPING HIS PLANET. MESOLITHIC AGE. (FROM 20 TO 9 – 8 THOUSANDS BC. GLACIERS RECEIVE THE ARISE OF BELIEF IN SIGNS, FETISHISM. THE APPEARANCE OF FUNERAL RITUALS AND BELIEF IN HIGHER POWERS. APPEARANCE OF SHAMANS, PRIESTS. POPULATION - 10 MILLION. APPROPRIATING TYPE OF ECONOMY – HUNTING, GATHERING , FISHING. MAN’S ENTRY INTO AMERICA AND AUSTRALIA. THE ADVANCE OF A NEW STAGE IN THE KNOWLEDGE OF THE WORLD: ROCK PAINTING, RITES OF MAGIC ABSTRACT THINKING. THE BIGGEST MYSTERY IS MAN HIMSELF WITH HIS INTELLECTUAL DEVELOPMENT.
MAN IS DEVELOPING HIS PLANET. MESOLITHIC AGE. (FROM 20 TO 9 – 8 THOUSANDS BC. GLACIERS RECEIVE THE ARISE OF BELIEF IN SIGNS, FETISHISM. THE APPEARANCE OF FUNERAL RITUALS AND BELIEF IN HIGHER POWERS. APPEARANCE OF SHAMANS, PRIESTS. POPULATION - 10 MILLION. APPROPRIATING TYPE OF ECONOMY – HUNTING, GATHERING , FISHING. MAN’S ENTRY INTO AMERICA AND AUSTRALIA. THE ADVANCE OF A NEW STAGE IN THE KNOWLEDGE OF THE WORLD: ROCK PAINTING, RITES OF MAGIC ABSTRACT THINKING. THE BIGGEST MYSTERY IS MAN HIMSELF WITH HIS INTELLECTUAL DEVELOPMENT.
 TRY TO Draw your own conclusions. MAIN CONCLUSIONS. THE ORIGIN OF HUMAN WAS THE RESULT OF A MULTIFACTORY INFLUENCE ON HIS DEVELOPMENT. EACH NEW STEP WAS CONNECTED WITH BOTH THE IMPROVEMENT OF WORK TOOLS AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE BRAIN. THE FIRST STAGE OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT IS THE EARLY PALEOLITHIC. THE MANUFACTURE OF TOOLS AND THE USE OF FIRE SEPARATED MAN FROM THE ANIMAL WORLD. THE BASIC RACES ARE BEING FORMED. IN THE MESOLITHIC ERA, MAN COVERED THE PLANET. . THE BRAIN DEVELOPES AND ABSTRACT THINKING ARISES: RITUALS, MAGIC, FETISHISM. SINCE THE PALEOLITHIC, THE CRO-MANNON MAN, THE MODERN TYPE OF HUMAN, HAS BEEN DOMINANT.
TRY TO Draw your own conclusions. MAIN CONCLUSIONS. THE ORIGIN OF HUMAN WAS THE RESULT OF A MULTIFACTORY INFLUENCE ON HIS DEVELOPMENT. EACH NEW STEP WAS CONNECTED WITH BOTH THE IMPROVEMENT OF WORK TOOLS AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE BRAIN. THE FIRST STAGE OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT IS THE EARLY PALEOLITHIC. THE MANUFACTURE OF TOOLS AND THE USE OF FIRE SEPARATED MAN FROM THE ANIMAL WORLD. THE BASIC RACES ARE BEING FORMED. IN THE MESOLITHIC ERA, MAN COVERED THE PLANET. . THE BRAIN DEVELOPES AND ABSTRACT THINKING ARISES: RITUALS, MAGIC, FETISHISM. SINCE THE PALEOLITHIC, THE CRO-MANNON MAN, THE MODERN TYPE OF HUMAN, HAS BEEN DOMINANT.
 NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION. BASIC CONCEPTS: NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION, PRODUCING TYPE OF ECONOMY, DIVISION OF LABOR, EXCHANGE, MONEY, PROPERTY INEQUALITY, MATRIARCHY AND PATRIARCHY, PROPERTY, TRIBE, CLAN, UNION OF TRIBES, ENEOLITHIC, METAL PROCESSING.
NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION. BASIC CONCEPTS: NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION, PRODUCING TYPE OF ECONOMY, DIVISION OF LABOR, EXCHANGE, MONEY, PROPERTY INEQUALITY, MATRIARCHY AND PATRIARCHY, PROPERTY, TRIBE, CLAN, UNION OF TRIBES, ENEOLITHIC, METAL PROCESSING.
 MAN AND NATURE: THE FIRST CONFLICT. NEOLITHIC – TRANSITION TO AGRICULTURE AND CASTLE BREEDING IN 9 – 8 THOUSAND. BC THE DEVELOPMENT OF AGRICULTURE AND CASTLE BREEDING ONLY IN FAVORABLE CONDITIONS: CASTLE BREEDING FROM HUNTING AND AGRICULTURE FROM GATHERING. THERE WAS A TRANSITION FROM THE APPROPRIATING TO THE PRODUCING TYPE OF ECONOMIC ACTIVITY. THE REASONS FOR THIS WERE THE IMPROVEMENT OF HUNTING GEARS AND THE CONSEQUENTIAL NUTRITION CRISIS THAT AFFECTED HUMAN COMMUNITIES. 1. SOME TRIBES LIMITED CONSUMPTION BY THE TABOO SYSTEM AND FROZEN IN THEIR DEVELOPMENT. 2. BREAKTHROUGH TO A NEW QUALITY IMPACT ON NATURE.
MAN AND NATURE: THE FIRST CONFLICT. NEOLITHIC – TRANSITION TO AGRICULTURE AND CASTLE BREEDING IN 9 – 8 THOUSAND. BC THE DEVELOPMENT OF AGRICULTURE AND CASTLE BREEDING ONLY IN FAVORABLE CONDITIONS: CASTLE BREEDING FROM HUNTING AND AGRICULTURE FROM GATHERING. THERE WAS A TRANSITION FROM THE APPROPRIATING TO THE PRODUCING TYPE OF ECONOMIC ACTIVITY. THE REASONS FOR THIS WERE THE IMPROVEMENT OF HUNTING GEARS AND THE CONSEQUENTIAL NUTRITION CRISIS THAT AFFECTED HUMAN COMMUNITIES. 1. SOME TRIBES LIMITED CONSUMPTION BY THE TABOO SYSTEM AND FROZEN IN THEIR DEVELOPMENT. 2. BREAKTHROUGH TO A NEW QUALITY IMPACT ON NATURE.
 Excess production caused not only trade, but also the emergence of wealth inequality. Gradually, leaders and AGRICULTURAL-PASTORAL CULTURES. sorcerers began to accumulate property and valuables. THE FIRST AGRICULTURAL CIVILIZATIONS. (7 – 4 THOUSAND B.C.) THE DIVISION OF LABOR DEPTHENED: AGRICULTURE SEPARATED FROM CASTLE BREEDING, CRAFT BECAME INDEPENDENT. THE SPHERE OF EXCHANGE WAS EXPANDING: VARIOUS CONNECTIONS OF NATURAL EXCHANGE BEGAN TO BE REPLACED BY MONEY. THESE CIVILIZATIONS ARE SOMETIMES CALLED RIVER CIVILIZATIONS (MILD CLIMATE, SOIL AND WATER) - EGYPT, INTERFLIVE, INDUS VALLEY, JUANGE. THE FIRST PLANTS: WHEAT, BARLEY, CORN IN THE INCA. HUGE CHANGES HAVE HAPPENED IN PEOPLE'S LIFE, IF BEFORE A PERSON'S ENTIRE LIFE WAS DEDICATED TO SURVIVAL AND A PERSON EXPILED FROM THE TRIBE WAS DOOMED, THEN WITH THE APPEARANCE OF THE PRODUCTION TYPE OF ECONOMY IT BECAME POSSIBLE TO PRODUCE MORE FOOD CUTS, WHAT YOU NEED
Excess production caused not only trade, but also the emergence of wealth inequality. Gradually, leaders and AGRICULTURAL-PASTORAL CULTURES. sorcerers began to accumulate property and valuables. THE FIRST AGRICULTURAL CIVILIZATIONS. (7 – 4 THOUSAND B.C.) THE DIVISION OF LABOR DEPTHENED: AGRICULTURE SEPARATED FROM CASTLE BREEDING, CRAFT BECAME INDEPENDENT. THE SPHERE OF EXCHANGE WAS EXPANDING: VARIOUS CONNECTIONS OF NATURAL EXCHANGE BEGAN TO BE REPLACED BY MONEY. THESE CIVILIZATIONS ARE SOMETIMES CALLED RIVER CIVILIZATIONS (MILD CLIMATE, SOIL AND WATER) - EGYPT, INTERFLIVE, INDUS VALLEY, JUANGE. THE FIRST PLANTS: WHEAT, BARLEY, CORN IN THE INCA. HUGE CHANGES HAVE HAPPENED IN PEOPLE'S LIFE, IF BEFORE A PERSON'S ENTIRE LIFE WAS DEDICATED TO SURVIVAL AND A PERSON EXPILED FROM THE TRIBE WAS DOOMED, THEN WITH THE APPEARANCE OF THE PRODUCTION TYPE OF ECONOMY IT BECAME POSSIBLE TO PRODUCE MORE FOOD CUTS, WHAT YOU NEED
 TRANSITION FROM MATRIARCHY TO PATRIARCHY. OWNERSHIP, ACCUMULATION OF KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS HAVE LEADED TO CHANGES IN THE CHANGE OF LIFE. NEOLITHIC PEOPLE LIVED IN LARGE FAMILIES. GIRLS WERE GIVEN IN MARRIAGE TO OTHER CLANDS AND TRIBES. THE MEN STAYED WITH THE FAMILY. DEGREE OF RELATIONSHIP IN THE MALE LINE AND HENCE THE ARISE OF PROPERTY. SEVERAL KINDS OF TRIBE. THE APPEARANCE OF A FAMILY HAS HAPPENED. THE QUESTION OF THE ORIGIN OF THE FAMILY HAS BEEN CONTROVERSIAL FOR A LONG TIME. ACCORDING TO MORGAN (USA) – THE FORMATION OF A FAMILY HAS PASSED SEVERAL STAGES. IN CONDITIONS OF HUNTING AND GATHERING - THE MAIN FIGURE IS A WOMAN WHO TRANSFERED EXPERIENCE AND ORGANIZED THIS BUILDING - MATRIARCHY WITH THE ADVANCE OF AGRICULTURE AND CASTLE BREEDING THE MORTALITY AMONG MEN DECREASED AND THEY CARRIED OUT THE MOST HARD AND IMPORTANT WORK. ALL THIS LEADED TO THE NORM OF PATRIARCHY – A SPECIAL ROLE FOR MEN IN SOCIETY.
TRANSITION FROM MATRIARCHY TO PATRIARCHY. OWNERSHIP, ACCUMULATION OF KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS HAVE LEADED TO CHANGES IN THE CHANGE OF LIFE. NEOLITHIC PEOPLE LIVED IN LARGE FAMILIES. GIRLS WERE GIVEN IN MARRIAGE TO OTHER CLANDS AND TRIBES. THE MEN STAYED WITH THE FAMILY. DEGREE OF RELATIONSHIP IN THE MALE LINE AND HENCE THE ARISE OF PROPERTY. SEVERAL KINDS OF TRIBE. THE APPEARANCE OF A FAMILY HAS HAPPENED. THE QUESTION OF THE ORIGIN OF THE FAMILY HAS BEEN CONTROVERSIAL FOR A LONG TIME. ACCORDING TO MORGAN (USA) – THE FORMATION OF A FAMILY HAS PASSED SEVERAL STAGES. IN CONDITIONS OF HUNTING AND GATHERING - THE MAIN FIGURE IS A WOMAN WHO TRANSFERED EXPERIENCE AND ORGANIZED THIS BUILDING - MATRIARCHY WITH THE ADVANCE OF AGRICULTURE AND CASTLE BREEDING THE MORTALITY AMONG MEN DECREASED AND THEY CARRIED OUT THE MOST HARD AND IMPORTANT WORK. ALL THIS LEADED TO THE NORM OF PATRIARCHY – A SPECIAL ROLE FOR MEN IN SOCIETY.
 TRANSITION TO THE ENEOLITHIC. POPULATION GROWTH LEADED TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF NEW TERRITORIES, AND A NEW STAGE IN HUMAN HISTORY BEGAN, CONNECTED WITH THE APPEARANCE OF THE FIRST STATES. TRIBAL ALLIANCES APPEARED, WHICH GRADUALLY LOST CONNECTION WITH EACH OTHER. THE APPEARANCE OF DIFFERENT LANGUAGES (5 – 4 THOUSAND B.C.) TOTAL 4 THOUSAND. LANGUAGES. INDO-EUROPEAN FAMILY OF LANGUAGES, FINNO-UGRIAN, MONGOLIAN, SEMITO-HAMIC, BERBERO-LIBYAN, CUSHITE, SINO-TIBETAN AND OTHERS. AT THIS TIME THE TRANSITION TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF METALS BEGINS: COPPER, TIN, LEAD AND OTHERS. DEVELOPMENT TIME: 7 THOUSAND. , BUT WIDE DEVELOPMENT IN 4 – 3 THOUSAND. BC IN THE ENEOLITHIC ERA (COPPER - STONE AGE)
TRANSITION TO THE ENEOLITHIC. POPULATION GROWTH LEADED TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF NEW TERRITORIES, AND A NEW STAGE IN HUMAN HISTORY BEGAN, CONNECTED WITH THE APPEARANCE OF THE FIRST STATES. TRIBAL ALLIANCES APPEARED, WHICH GRADUALLY LOST CONNECTION WITH EACH OTHER. THE APPEARANCE OF DIFFERENT LANGUAGES (5 – 4 THOUSAND B.C.) TOTAL 4 THOUSAND. LANGUAGES. INDO-EUROPEAN FAMILY OF LANGUAGES, FINNO-UGRIAN, MONGOLIAN, SEMITO-HAMIC, BERBERO-LIBYAN, CUSHITE, SINO-TIBETAN AND OTHERS. AT THIS TIME THE TRANSITION TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF METALS BEGINS: COPPER, TIN, LEAD AND OTHERS. DEVELOPMENT TIME: 7 THOUSAND. , BUT WIDE DEVELOPMENT IN 4 – 3 THOUSAND. BC IN THE ENEOLITHIC ERA (COPPER - STONE AGE)
 MAIN CONCLUSIONS. APPROXIMATELY 10 THOUSAND. BC THERE WAS A CRISIS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF CIVILIZATION, CONNECTED WITH THE EXHAUSTION OF HUNTING AND GATHERING POSSIBILITIES. THE WAY OUT OF IT IN TWO WAYS: 1. LIMITING NEEDS 2. DEVELOPMENT OF AGRICULTURE AND CASTLE BREEDING. THE PRODUCTION TYPE OF ECONOMY LEAD TO CHANGES IN THE WAY OF LIFE: DIVISION OF LABOR, CRAFT PRODUCTION, EXCHANGE AND APPEARANCE OF MONEY. THERE IS A TRANSITION FROM MATRIARCHY TO PATRIARCHY AND THE FORMATION OF A FAMILY. THE CONCEPT OF PROPERTY APPEARS. WITH THE GROWTH OF THE POPULATION, PEOPLE SPREAD TO NEW PLACES AND, AS A RESULT, DIFFERENT LANGUAGES APPEAR. EXACTLY AT THIS TIME AT 7 THOUSAND. BC THE EXPLORATION OF METALS BEGINS. PERIOD FROM 4 TO 3 THOUSAND. BC IS CALLED THE COPPER - STONE AGE (ENEOLITHIC) A NEW STAGE BEGINS, RELATED TO THE ARISE OF STATES.
MAIN CONCLUSIONS. APPROXIMATELY 10 THOUSAND. BC THERE WAS A CRISIS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF CIVILIZATION, CONNECTED WITH THE EXHAUSTION OF HUNTING AND GATHERING POSSIBILITIES. THE WAY OUT OF IT IN TWO WAYS: 1. LIMITING NEEDS 2. DEVELOPMENT OF AGRICULTURE AND CASTLE BREEDING. THE PRODUCTION TYPE OF ECONOMY LEAD TO CHANGES IN THE WAY OF LIFE: DIVISION OF LABOR, CRAFT PRODUCTION, EXCHANGE AND APPEARANCE OF MONEY. THERE IS A TRANSITION FROM MATRIARCHY TO PATRIARCHY AND THE FORMATION OF A FAMILY. THE CONCEPT OF PROPERTY APPEARS. WITH THE GROWTH OF THE POPULATION, PEOPLE SPREAD TO NEW PLACES AND, AS A RESULT, DIFFERENT LANGUAGES APPEAR. EXACTLY AT THIS TIME AT 7 THOUSAND. BC THE EXPLORATION OF METALS BEGINS. PERIOD FROM 4 TO 3 THOUSAND. BC IS CALLED THE COPPER - STONE AGE (ENEOLITHIC) A NEW STAGE BEGINS, RELATED TO THE ARISE OF STATES.
 SOURCES ZAGLADIN N.V. WORLD HISTORY OF RUSSIA AND THE WORLD FROM ANCIENT TIMES TO THE END OF THE 19TH CENTURY: TEXTBOOK FOR 10TH GRADE. – 7 - IZD. – M.: TID “RUSSIAN WORD - RS”, 2007. CHAPTER 2. “PRIMIMEVAL AGE”
SOURCES ZAGLADIN N.V. WORLD HISTORY OF RUSSIA AND THE WORLD FROM ANCIENT TIMES TO THE END OF THE 19TH CENTURY: TEXTBOOK FOR 10TH GRADE. – 7 - IZD. – M.: TID “RUSSIAN WORD - RS”, 2007. CHAPTER 2. “PRIMIMEVAL AGE”

PALEOLITHIC PALEOLITHIC (from pareo... and Greek lithos stone), the ancient Stone Age, the first period of the Stone Age, the time of the existence of fossil man (pareoanthropus, etc.), who used chipped stone, wooden, bone tools, was engaged in hunting and gathering. The Paleolithic lasted from the emergence of man (over 2 million years ago) until approximately the 10th millennium BC. e. The most important achievement of the pareolithic was mastering the ability to use fire (about a thousand years BC). Making a fire.

At the end of the Early Pareolithic era, a period of sharp changes in the natural conditions of existence of primitive people began. Many herds of primitive hunters - Neanderthals were unable to adapt to new natural conditions. By the end of the Early Pareolithic (about a thousand years BC), Neanderthals completely disappeared. The modern, Cro-Magnon type of man has established himself everywhere. Stone tip with a “foot”. Wed. pareolithic

Mesolithic era MESOLITHIC (from Meso... and Greek lithos stone), Middle Stone Age, transition from Pareolithic to Negolithic (c. 10th-5th millennium BC). In the Mesolithic, bows and arrows, microlithic tools appeared, and the dog was domesticated. The Mesolithic is sometimes also called protonegolith (from the Greek protos first and negolith) or epipareolithic (from the Greek epi after and pareolith).

The Mesolithic covers the period from the 20th to the 9th-8th millennium BC. e. Natural conditions at this time become more favorable, new territories become available for settlement. The population does not exceed 10 million people. Around this era, man first penetrated the American continent and Australia. During the Mesolithic era, rock painting arose and became widespread. An example of a complex weapon.

Rock carvings, scientifically called petroglyphs, are found in different parts of the world. They belong to different historical eras from the Pareolithic to the Middle Ages. Ancient people applied them to the walls and ceilings of caves, to open rock surfaces and individual stones. The oldest Pareolithic rock paintings were found in caves and grottoes in Southern France and Northern Spain. The rock carvings are characterized by figures of animals, primarily the objects of ancient man's hunt: bison, horses, mammoths, rhinoceroses; less common predators are bears and lions. Dance. Lleid painting. Spain. "Stone Newspaper" Arizona.

In Russia, petroglyphs were called pisanitsa. Here, pareolithic drawings were discovered in the Kapova Cave in the Urals and on the rocks near the village of Shishkino on the Lena River. Already in ancient times, the style and technique of rock paintings were varied, from outline drawings scratched on stone to bas-relief and polychrome painting, for which mineral paints were used. Rock paintings had magical meaning for ancient people. Fighting archers Composition in the Lascaux cave Paintings on a mountain plateau. Tassoli-Ajjer, Algeria.


Neolithic era NEOLITHIC (from it... and the Greek lithos stone), new Stone Age, period (about 1000 BC) of transition from an appropriating economy (gathering, hunting) to a producing one (agriculture, cattle breeding). In the Negolithic era, stone tools were polished, drilled, pottery, spinning, and weaving appeared. Primitive tools


1. Using the knowledge acquired in biology, history and social studies lessons, talk about the most common hypotheses of human origins. When did the theory of evolution arise and who was its author? What myths do you know that explain the origin of the world and man?
The main theories of the origin of man are divided into creationist (man was created thanks to the actions of higher forces) and evolutionary (man descended from other forms of life as a result of evolution).
Every religion has its own creationist myth. For example, the Bible says that the Lord created a man from clay and breathed spirit into him, and created a woman from a man’s rib. The ancient Greek poet Hesiod wrote about 5 generations of people who were successively created and destroyed by the gods. These are generations of gold, silver, copper people and a generation of heroes. According to Hesiod, the current generation is iron.
Evolutionary theory arose in the 19th century. The greatest contribution to the theory of the evolution of species of living beings was made by Charles Darwin, who was the first to substantiate the origin of humans from other animals (from primates).
2. What factors contributed to the separation of man from the natural world? What role did interspecific and intraspecific struggle play in the process of human evolution?
From the natural world, the first ancestors of man began to distinguish intelligence and the use of specially made tools. But over time, self-awareness became the main factor: a person thinks of himself separately from nature and his personality separately from the rest of the world, this determines all his behavior, and this is what sets him apart from all other living beings.
There are different theories as to what triggered the rapid evolution of the group of primates that led to the emergence of humans. According to the most common scenario, as a result of climate change, the habitat of this group became completely different in a short period of time: savannas formed in place of forests. Primates had to adapt to new conditions so quickly that evolution did not have time to make them stronger, faster, etc. Instead, they began to survive due to their intelligence and the use of their front limbs, which were already free from walking. At the same time, both interspecific and intraspecific struggle played a major role in human evolution. In competition with other species for food and the fight against predators, intelligence and skills in making tools were developed, so man could do nothing else to oppose the aggressive external environment. However, intraspecific competition also helped. Apparently, human ancestors chose partners for creating families not by strength or beauty, but by their ability to get more food for their offspring, which again required intelligence and the ability to make tools.
3. Name the directions of evolution of the human race. What was the significance of the accumulation of knowledge for ancient man in the struggle for survival?
Evolution of most animal species aims to change the animal's body to suit environmental conditions. Man instead evolved to create means of adaptation to the environment (tools) with his own hands, and, over time, to change the environment to suit his needs. For example, evolution changes the teeth of animals so that they can eat new foods; man instead learned to use fire and was able to process food so that it fits his teeth. Thus, the accumulation of knowledge had a decisive role in the survival of man as a biological species, because only knowledge helped to make increasingly complex tools, use fire and other devices, and ultimately reach the modern level of development.
4. Which regions are the ancestral home of humanity? Name the humanoid predecessors of humans.
The first tools were found in East Africa, North and South Asia. The immediate predecessor of modern humans is now considered to be the so-called Homo habilis.
5. At what stage of primitive history did human settlement take place across the continents of the planet?
Human settlement on the planet begins after the retreat of the glacier. People appeared in America ca. 25 thousand years ago, and Australia - approx. 20.
6. When did rock art and religious beliefs emerge in human groups? What function did they perform?
Cave painting appeared already among the Neanderthals (they lived in Europe 400-250 thousand years ago). At the same time, apparently, religious ideas also arose (burials were found that were clearly made using some kind of ritual). Rock painting, apparently, was also part of some rituals. For example, some of these drawings are related to astronomical phenomena. In modern humans, rock art has been known since the Mesolithic era (which lasted from the 20th to the 9th-8th centuries BC).
1. Using the knowledge acquired in biology, history and social studies lessons, talk about the most common hypotheses of human origins. When did the theory of evolution arise and who was its author? What myths do you know that explain the origin of the world and man?
The main theories of the origin of man are divided into creationist (man was created thanks to the actions of higher forces) and evolutionary (man descended from other forms of life as a result of evolution).
Every religion has its own creationist myth. For example, the Bible says that the Lord created a man from clay and breathed spirit into him, and created a woman from a man’s rib. The ancient Greek poet Hesiod wrote about 5 generations of people who were successively created and destroyed by the gods. These are generations of gold, silver, copper people and a generation of heroes. According to Hesiod, the current generation is iron.
Evolutionary theory arose in the 19th century. The greatest contribution to the theory of the evolution of species of living beings was made by Charles Darwin, who was the first to substantiate the origin of humans from other animals (from primates).
2. What factors contributed to the separation of man from the natural world? What role did interspecific and intraspecific struggle play in the process of human evolution?
From the natural world, the first ancestors of man began to distinguish intelligence and the use of specially made tools. But over time, self-awareness became the main factor: a person thinks of himself separately from nature and his personality separately from the rest of the world, this determines all his behavior, and this is what sets him apart from all other living beings.
There are different theories as to what triggered the rapid evolution of the group of primates that led to the emergence of humans. According to the most common scenario, as a result of climate change, the habitat of this group became completely different in a short period of time: savannas formed in place of forests. Primates had to adapt to new conditions so quickly that evolution did not have time to make them stronger, faster, etc. Instead, they began to survive due to their intelligence and the use of their front limbs, which were already free from walking. At the same time, both interspecific and intraspecific struggle played a major role in human evolution. In competition with other species for food and the fight against predators, intelligence and skills in making tools were developed, so man could do nothing else to oppose the aggressive external environment. However, intraspecific competition also helped. Apparently, human ancestors chose partners for creating families not by strength or beauty, but by their ability to get more food for their offspring, which again required intelligence and the ability to make tools.
3. Name the directions of evolution of the human race. What was the significance of the accumulation of knowledge for ancient man in the struggle for survival?
Evolution of most animal species aims to change the animal's body to suit environmental conditions. Man instead evolved to create means of adaptation to the environment (tools) with his own hands, and, over time, to change the environment to suit his needs. For example, evolution changes the teeth of animals so that they can eat new foods; man instead learned to use fire and was able to process food so that it fits his teeth. Thus, the accumulation of knowledge had a decisive role in the survival of man as a biological species, because only knowledge helped to make increasingly complex tools, use fire and other devices, and ultimately reach the modern level of development.
4. Which regions are the ancestral home of humanity? Name the humanoid predecessors of humans.
The first tools were found in East Africa, North and South Asia. The immediate predecessor of modern humans is now considered to be the so-called Homo habilis.
5. At what stage of primitive history did human settlement take place across the continents of the planet?
Human settlement on the planet begins after the retreat of the glacier. People appeared in America ca. 25 thousand years ago, and Australia - approx. 20.
6. When did rock art and religious beliefs emerge in human groups? What function did they perform?
Cave painting appeared already among the Neanderthals (they lived in Europe 400-250 thousand years ago). At the same time, apparently, religious ideas also arose (burials were found that were clearly made using some kind of ritual). Rock painting, apparently, was also part of some rituals. For example, some of these drawings are related to astronomical phenomena. In modern humans, rock art has been known since the Mesolithic era (which lasted from the 20th to the 9th-8th centuries BC).
At the origins of the human race. Neolithic Revolution
Lesson Objectives: Introduce students to hypotheses of human origin: find out what factors
contributed to the separation of man from the natural world; deepen existing ideas
about the nature and main components of the Neolithic revolution.
Equipment: map, computer presentation
During the classes:
I. Repetition
Exercise: Answer the questions
1. Name the historians of antiquity.
2. What are the features of historical descriptions of antiquity?
3. Name the features of studying history during the Middle Ages.
4. What is a historical source?
5. List the types of historical sources.
6. Name the theories of historical development known to you. Name their authors.
7. List the periods of world history.
II. Learning new material
Why is it necessary to know the history of primitive society?
Many phenomena of modern human life arose or began to arise in the hoary antiquity of primitive society. Homes, clothing, marriage and family, morality and etiquette, useful knowledge, art and religion, agriculture and cattle breeding, the basics of processing materials - to understand all this, you often have to go back to the origins. This is educational value primitive history.
Primitive history also has a great ideological significance . How did man appear on Earth: as a result of the evolution of organic nature or by divine providence? Or maybe human nature has alien origins? What is the origin of the human races? Does it give rise to racist ideas about their inferiority? Is man by nature a collective being? How and when did private property, inequality and the state emerge?
Knowledge of primitive history has practical significance . After all, many peoples of Asia, Africa, Latin America, and Oceania, until quite recently, were or continue to be at various stages of decomposition of the primitive communal system. The features and remnants of this system in their lives require analysis, evaluation, and accounting, and historical science does not stand aside from this.
Periodization of primitive history
There are several types of periodization of primitive history. Archaeological periodization as the main criterion it uses the sequential change of tools and materials from which they were made. Main stages: (slide 2)
It should be noted that the dating is very approximate, and different researchers offer their own options. In addition, we must remember that in different regions these stages occurred at different times.
Geological periodization
The history of the Earth is divided into four eras. Last era - Cenozoic . It is divided into tertiary (began 69 million years ago), quaternary (started 1 million years ago) and modern (started 14 thousand years ago) periods.
The Quaternary period is divided into Eopleistocene (pre-glacial period), Pleistocene (ice age) and Holocene (post-glacial period). (slide 3)
Anthropological periodization
Modern man constitutes a species sapiens(Latin - intelligent) of the genus Homo (Latin - man), belonging to the family hominid(people) squad primates.
The distant ancestor of humans is considered to be a group of anthropoid primates, called - Dryopithecus(tree monkeys).
The process of formation of Dryopithecus began 25 million years ago in the tropical and equatorial regions of Africa and Asia. They resembled modern baboons and chimpanzees.
Then, 5 - 6 million years ago, they appeared here Australopithecus – "ape people", which represented a transitional form from Dryopithecus to the most ancient people - Archanthropus. Australopithecines were distinguished by a relatively large brain volume (550 – 600 cubic cm) (slide 4)
Archanthropes (ancient people) – Homohabilis(lat. – skillful man), appeared about 600 - 500 thousand years ago. This Pithecanthropus (whose remains were found on the island of Java) brain volume is about 900 cubic meters. cm., Sinanthropus (found in China) brain volume is about 1050 cubic meters. see. However, the discovery of the English anthropologist and archaeologist Louis Leakey, made in Kenya, in the Olduvai Gorge, proved that the oldest man appeared about 2.5 million years ago, i.e. Archanthropus lived happily with Australopithecines for a long time. In addition, it was proven that Africa was the ancestral home of man. It was the human remains found in Olduvey that were given the species name Homohabilis. Over time, Homo habilis transformed into Homoerectus (upright or upright person). (slide 5 -6)
This became a new stage in human evolution. 300 - 250 thousand years ago the archanthropes were gradually replaced paleoanthropes (ancient people) - Homoerectus(Neanderthals – brain volume 1200 – 1600 cc cm. , Cro-Magnons ). (slide 7)
Near 100 thousand years ago the Earth's climate began to change. The temperature dropped significantly. With each century, the cold climate spread further and further into the continent. Gradually, the territory of Europe was covered by a huge glacier. Along with climate change, the flora and fauna of the planet changed. Many species of flora and fauna have disappeared forever. Only a few creatures managed to adapt to the new conditions of existence.) The harsh climate forced primitive people adapt and fight for your survival . (slide 8)
45 - 40 thousand years ago, paleoanthropes were finally replaced by neoanthropes - Homosapiens
(homo sapiens) – brain volume 1400 – 1500 cubic meters. cm., which include
modern people. (slide 9)
The process discussed above—the process of human formation from anthropoid ancestors to modern humans—is called anthropogenesis . (slide 10)
Anthropogenesis- the process of human formation from anthropoid ancestors to modern humans
The settlement of people and the formation of races
At the last stage of anthropogenesis occurs raceogenesis formation of human races. This process is associated with human settlement and its adaptation to the natural and climatic conditions of various regions of the Earth.
The original territory of the emergence of man was within the equatorial and tropical zones of Africa and Asia, and from here his spread across the Earth began.
People settled throughout the African continent. About 1 million years ago, archanthropes moved to the northern regions and reached the temperate zone of Europe. Their descendants - paleoanthropes - have already settled in most of Europe.
In Asia, the main areas of origin of primitive people were within the Sunda Islands, India, and China.
What points of view exist regarding the settlement of America and Australia?
1) Population of America and Australia autochthonous, i.e. is the indigenous, original population.
2) People came to America and Australia from Asia. And apparently they came by land. Since the level of the World Ocean was then lower, there was an isthmus of land in place of the Bering Strait. And Australia, the islands of the Malay and Sunda archipelagos and the island of Tasmania could form a single whole with the mainland. The decrease in the level of the World Ocean by about 100 m was due to the fact that a large amount of moisture was conserved in glaciers. This led to the drying of shallow sea waters and the emergence of land crossings between continents.
3) The first two versions arose because for a long time it was believed that primitive people could not overcome the vast expanses of water separating America, Australia and Oceania from Eurasia on their imperfect boats and rafts. But the traveler Thor Heyerdahl was able to swim across the Pacific Ocean on a homemade raft and put forward the version that Primitive people could get to America not only by land, but also by swimming across the ocean.
It can be argued that by the end of the Paleolithic, all continents except Antarctica were inhabited by people. Having adapted to extreme conditions of existence, man began to live in all natural zones. As humans adapted to their environment, morphological and physiological differences gradually began to appear between the inhabitants of different regions of the globe. This is how three large groups of races appeared, which have survived practically unchanged to the present day.
The time of formation of human races, as well as the formation of modern man, dates back to Late Paleolithic.
The mixing of races was of great importance in the process of race formation, as a result of which transitional intermediate racial types began to form.
Neolithic Revolution
(slide 11 - 14)
However, further improvement of hunting tools led to the extermination of many species of animals and a reduction in their numbers. As a result, primitive man was threatened with famine and extinction. This situation prevailed at the beginning of the 10th millennium BC. scientists call the first crisis in the development of civilization .
This forced people to search for a way out of the crisis - people began to move to a new level of development, which was accompanied by a conscious impact on the natural environment and its transformation.
So people noticed that breeding animals in captivity can be much more productive and safer than hunting their wild relatives. This observation marked the beginning of the development of cattle breeding.
The same thing happened with agriculture. Over time, through observation and experience, people came to understand that the seeds of collected wild plants could be sown near the settlement and get a much larger harvest than collecting plants through foraging. This is how it came about:
1st division of labor: division into farmers and cattle breeders.
However, one should not think that the transition from an appropriating to a producing economy was a simple, quick and widespread matter.
The development of cattle breeding and agriculture occurred only in favorable natural conditions. Moreover, it took millennia for breeds of fully domesticated animals to emerge that were completely different from their wild ancestors; for plant cultivation.
The development of agriculture led to sedentarization, and the increase in labor productivity contributed to the gradual expansion of the community. The first large settlements, and then cities, appeared in Western Asia and the Middle East.
Truly revolutionary changes occurred as a result of the development of metals. People master the first alloy of copper and tin - bronze. In the 5th – 4th millennia BC. Weaving and pottery developed, boats and the first wheeled carts appeared, driven by draft animals (horses, donkeys, oxen). Man realized: the second division of labor.
2nd division of labor: highlighting crafts as a separate branch of the producing economy.
(slide 15)
Neolithic Revolution – transition from the primitive (appropriating) economy of hunters and
gatherers to a productive economy based on agriculture
and cattle breeding.
(slide 16-17)
Exercise: Fill the table
| STONE AGE | PALEOLITHIC | MESOLITHIC | NEOLITHIC |
||||||||
| CHRONOLOGICAL FRAMEWORK | Early Paleolithic: | Middle Paleolithic: 300 – 40 thousand years BC | 10 thousand years BC | 10 – 4 thousand years BC |
|||||||
| REPRESENTATIVES | Homohabilis(skillful person): | Homoerectus | Homosapiens |
||||||||
| MAIN ACTIVITIES | |||||||||||
| TOOLS LABOR | |||||||||||
| PUBLIC ORGANIZATION | |||||||||||
| SPIRITUAL CULTURE | |||||||||||
| STONE AGE | PALEOLITHIC | MESOLITHIC | NEOLITHIC |
||||||||
| CHRONOLOGICAL FRAMEWORK | Early Paleolithic: 2.5 million – 300 thousand years BC | Middle Paleolithic: 300 – 40 thousand years BC | Late Paleolithic: 40 - 10 thousand years BC. | 10 thousand years BC | 10 – 4 thousand years BC |
||||||
| REPRESENTATIVES | Homohabilis(skillful person): Pithecanthropus, Sinanthropus - Archanthropus (ancient people) | Homoerectus(homo erectus) – Neanderthal (paleoanthropus – ancient man) | Homosapiens(homo sapiens) – Cro-Magnon, a modern type of person |
||||||||
| MAIN ACTIVITIES | Appropriating type of economy: gathering, driven hunting, the beginning of mastering fire and making clothes | Appropriating type of economy: gathering, individual hunting, domestication of animals | Producing type of economy (Neolithic revolution): the beginning of agriculture, cattle breeding |
||||||||
| TOOLS LABOR | Primitive: hand axes, scrapers, wooden spears with burnt tips, piercings | Bow and arrows, composite weapons: axes, harpoons, spears with tips | Improving existing hunting tools, potter's wheel, loom, drills, hoe, sickle |
||||||||
| PUBLIC ORGANIZATION | Ancient community: collectivism, equality | Tribal community | Neighborhood community: wealth inequality, tribal leaders, sacralization of power |
||||||||
| SPIRITUAL CULTURE | Thinking | Magical and funeral rituals | Intelligence, developed speech, magic: animism, totemism, magical images of animals | Cult of ancestors and leaders, cult of the progenitor mother |
|||||||
Homework: §4 -5, table








